3d Modeling And Use of Animation in
Industrial Facilities
Prof.Dr. Kamuran GÜÇLÜ,
Prof.Dr., Kamuran.guclu@gedik.edu.tr,
Asc.Dr. Kayhan
KAPLAN,
Asc.Dr., kayhankaplan@hotmail.com,
Seda Muratoğlu,
sdmuratoglu@gmail.com
Gedik University Faculty of Architecture and Fine Arts. Istanbul/Turkey
By the development of technology, the usage of three dimensional (3D)
images which are created by computers
are increasing in all areas. 3D technology which is used in Industrial facilities
for many years, reached the final point with animations and simulations. This
study was carried out in Gedik Casting Welding factory in Istanbul (Turkey).
All factory with an area of 25,000 m2,
is modeled in three-dimensional by a computer realistically. Also manufacture
and production process in the factory animated in real-time. Results of this
study are used for different purposes. First, the animation of production
process revealed the advantages and disadvantages of the factory in terms of efficiency
and planning. This study will be an important guide for establishing these
types of facilities in the factory. On the other hand these high-quality images
and animations can be used in both national and international advertisement of
the factory. Thus, the opportunity to feel being in factory and evaluation will
be provided without visiting the factory.
Introduction
In parallel with the development of Information Technology, new ones are
being added to the graphic processes realized by three-dimensional cards (Alpha
blending, Environment mapping, Fogging, Shading, Gouraud shading, Lens flaring,
Texture mapping, Mip mapping). While the computer games are shown as the
propulsive force in the development of the three dimensional technology in the
personal computers today, in the near future, three dimensional applications
will be a part of the operating system and the business applications will be
three dimensional as well (Kaplan
et al., 2009).
Three-dimensional (3D) visualization of simulation results is an important
and useful technique for engineering simulation (Rohrer, 2000). It allows users
to examine the complex processes of production plants in real-time and from
different aspects. 3D visualization represents physical working environments
with 3D graphics objects, and presents abstract simulation models by means of
computer animation. It produces the visual presentation of what is to happen in
the real world, thus providing users with a facility to study and analyze the
production and logistics behaviors of industrial manufacturing operations
(Zhong and Yuan, 2011). Through 3D visualization, users can obtain information
not only from reports and statistical results, but also from the visual
scenarios of the entire operational cycle within production plants, including
supply chains, inventory, resource utilization, flow of materials, and the
overall operation.
1.
Field of Study
This study
was carried out in Gedik Casting and
Valve Factory; Istanbul-Turkey. Gedik Casting Factory is located in Hendek Organized
Industrial Zone where is 160 km far from Istanbul City Center. Factory has
25.000 m2 covered area and 25.000 m2 open area
(figure 1). Iron casting, Spheriodal Graphite Cast Iron, Steel and
Stainless Steel, Bronze and Sand Casting products were manufactured in this
factory.
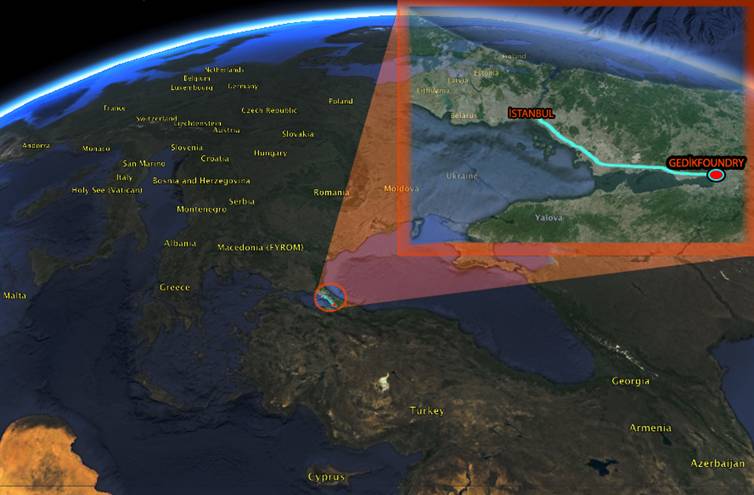
Fig. 1. Gedik Casting
Factory and Location
This factory
is established 4 main modules: Sand Preparation System, Sinto Casting Line,
Melting Furnace, Cleaning and Grinding.
These modules
also work with Core room, Dust Collection Systems, Furnace Systems. Manufacture
capacity of the factory is 25.000 tones per year.
Factory
Features and modeled departments:
• Horizontal flaskless molding line with capacity of 250 mould/hour.
• Steel casting automatic molding up to 400 kg with resin-cored molding.
• Cooling and sorting conveyor system for effective casting handling.
• Two fully automated independence sand plants.
• Steel Casting: single piece: 10 - 1.000 kg.
• With the size of the mold with a molding machine 500x600x250/250mm.
• FBOX III Unrated weighs 1kg-50kg cast iron (figure 2).
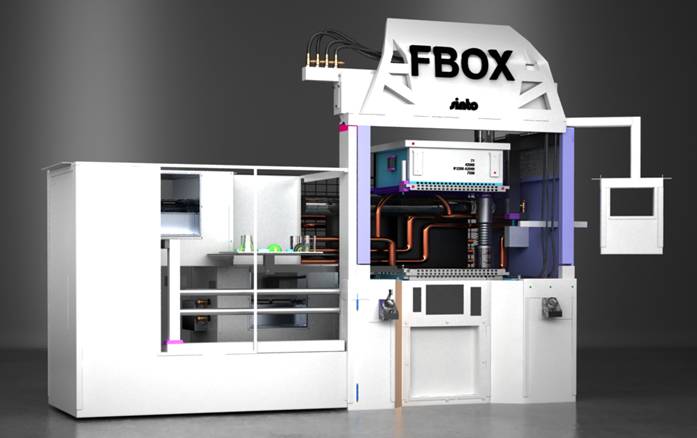

Fig. 2. Fbox:
photorealistic modeled
• Large parts of the molding is possible of except that FTL.
• Ductile iron can be cast in one piece up to 2000 kg.
• 4 medium frequency induction furnaces.
• Machining workshop capabilities.
• Automatic continues grinding and trimming system.
• Fully equipped metallurgical laboratories and NDT.
• MFOuUllyLDeqINuiGppLeIdNEmSetallurgical laboratories and NDT.
• 2 FBOX-III flaskless molding lines with the dimensions of 500X600x250
[mm].
• 1 box-shaped molding line with the dimensions of 1000X800X300[mm].
• 1 FTL (steel casting) alphaset resin sand molding line.
• Core: The cores are made by Shell and Cold Box Core Machines.

Fig. 3. Fbox line
modeled
2. Method
Research was commenced primarily with the modeling of Gedik Casting
Factory. This long-run research required bringing together different methods
since it was based on a study that had scientific, social, and aesthetical features.
With this objective in my mind, a path in the form of Data Collection,
Analysis, Modeling, Overlying, and Rendering was followed. Modeled in the
Factory of Gedik Casting is shown in Figure 2.
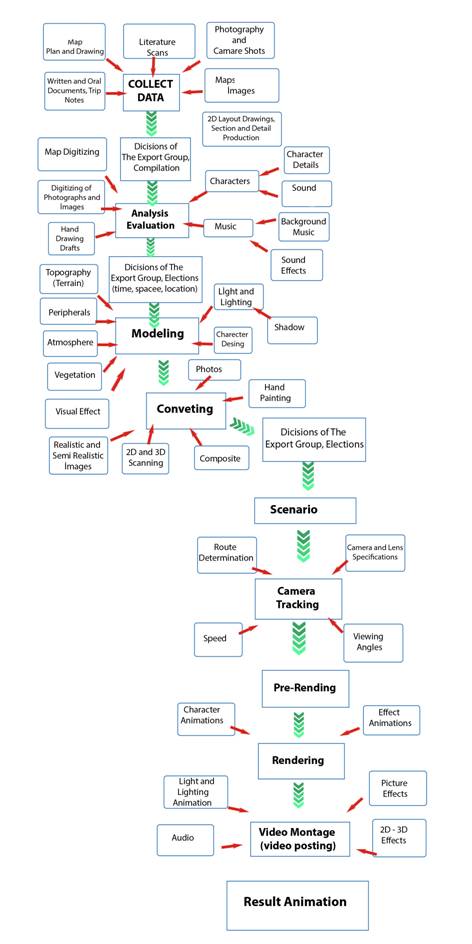
Fig. 4. Flow
chart of the study
3. Process Modeling and Animation
In the research, the structures that would be primarily modeled were
selected and their source information was gathered.
Location of
the factory was modeled 3D according to existing CAD Project. The usage of open
areas and passage implementation is visualized with flora (figure 5,6). All
fields and machines in the factory were modeled realistically.

Fig. 5. Gedik
Casting general model

Fig 6. Gedik
Casting outdoor model
To present animation more
realistic, kinematic characters added to scene. All levels in the production
animated separately. Modeled characters, were animated according to their task
in the factory. (Figure 5,6).
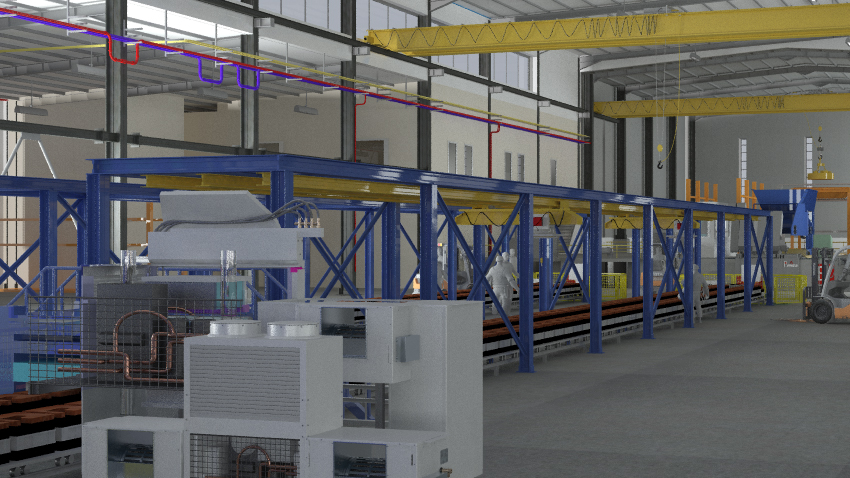

Fig. 7. Factory
interior model 1
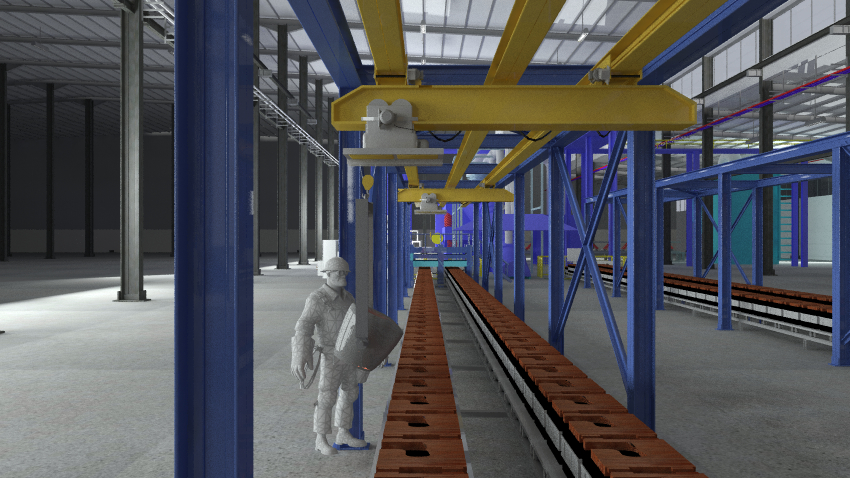

Fig. 8. Factory
interior model 2
Conclusion
The research is important as it covers different fields of science like
archaeology, landscape planning, provincial planning, and computer-supported
animation. It is an original project thanks specifically to the utilization of
different scientific methods and the convergence of the software programs used
for different areas like remote detection, solid modeling, and animation the
research, the structures that would be primarily.
Results of this study are used for different purposes. First, the animation
of production process revealed the advantages and disadvantages of the factory
in terms of efficiency and planning.
This study will be an important guide for establishing these types of
facilities in the factory. On the other hand these high-quality images and
animations can be used in both national and international advertisement of the
factory (figure 9). Thus, the
opportunity to feel being in factory and evaluation will be provided without
visiting the factory.
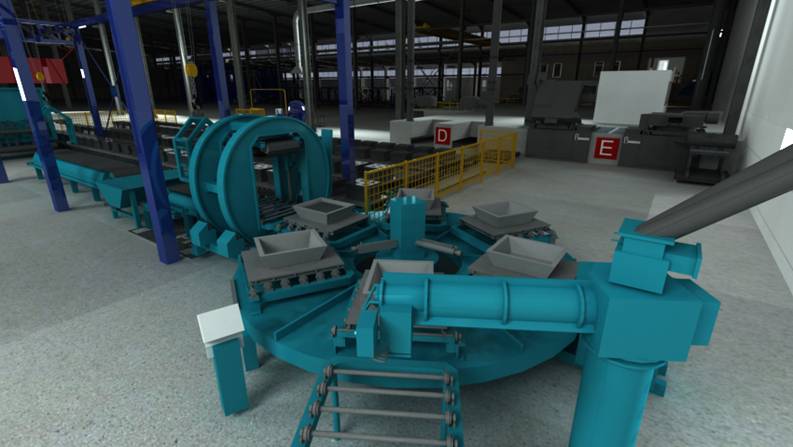

Fig. 9. Process
animation
References
1. Kaplan, K., Pamir, H.,
& Parlar, T. (2009). Antik Kent ve Çevrelerinin
Görselleştirilmesi, Modellenmesi, ve Animasyonu ile Gerçek
Zamanlı Render Motorlarının Kullanımı: Antakya Kenti
Örneği. Ankara TUBITAK Proje No: 107278
2. Rohrer, M. W. (2000).
Seeing is believing: The importance of visualization in manufacturing
simulation, Proceedings of the 2000 Winter Simulation Conference, 1211-1216.
3.
Zhong, Y., Yuan, X., (2004). 3D visualization of discrete
event simulation and its applications in virtual manufacturing. International
Journal of CAD/CAM. 4 (1): pp. 19-32.